Solar Panels

Solar Panels, Their Definition, and Their Materials, and Their Parts
A solar panel (a photovoltaic panel) is an interlocking group of photovoltaic cells ( solar cells). Solar cells produce electricity when exposed to sunlight (solar power). In 1981, Martin Green found that a solar cell produce 0.51 V (Volt) of voltage, to output 0.7 W (Watt) of electricity. Cumulative solar PV capacity will reach 1500 GW by 2027, according to the International Energy Agency.
Solar panels are a bunch of solar cells. Solar cells are mainly made of silicon. Solar cells are receivers of sunlight. They are connected within a specific framework to form solar panels.
PV panels are made of 7 materials including 76% glass, 10% polymer, 8% aluminum. Those material make different component and parts of solar panels (Silicon Wafers, Frames, Anti-reflective Coating).
Silicon solar panels were first invented in the 1800s. In the 1950s, scientists developed solar panels’ parts that were more efficient enough to be practical. Since that time, solar panels have developed significantly and have many types and kinds.
Solar panels have 4 main types (Bifacial solar panels, Thin film solar panels, Monocrystalline solar panels, Passivated Emitter and Rear Cell (PERC)). 5 different kinds of solar panels are used in solar systems including (Transparent solar panels, Shingled solar panels, Solar trees).
In all types, solar panels are combined to form the solar array. A solar panel system is created when a solar array is connected to some devices, such as inverters, batteries, tracking systems. Then, solar systems work to converts sunlight into electricity for homes, commercial buildings, and farms.
This article answers questions like What are solar panels? What are solar panels made of? How do solar panels work? What are solar arrays? How to install a Solar Array? What are Home Solar Panel Systems? How do Solar Panels Work ? What are Solar Panels Usages? Are solar panels recyclable? And more.
The following figure shows a solar cell, a solar panel, string solar panels, and a solar array.

What are Solar Panels?
Solar panels (photovoltaic panels (PV)) are devices that convert sunlight into electricity. Solar panels consist of multiple solar cells made from semiconductor materials like silicon. Solar cells absorb photons from sunlight to generate an electric current.
Solar panels utilise sunlight (solar power) to generate electricity without additional fuel or energy input. This makes solar panels a renewable and environmentally friendly source of electricity.
Solar panels provide clean and renewable energy. Solar panels are the third largest clean energy system. In 2022, Solar PV systems generated 4.5% of total global electricity which is more than solar systems production in 2021 by 26%, according to the International Energy Agency.
Solar panels are made of a different percentage of essential materials (glass, polymer, silicon, and others) that work to achieve a high conversion efficiency to generate electricity. Those materials make different parts of solar panels (Silicon Wafers, Metal Contacts, Encapsulation Materials, and many others).
Solar panels materials combination was invented in 1881 by Charles Fritts the American inventor.
What are Solar Panels Made of?
Crystalline silicon solar panels (Monocrystalline, Polycrystalline) are made of 76% glass, 10% polymer, 8% aluminum, 5% silicon, 1% copper, less than 0.1% silver and other metals, according to the International Renewable Energy Agency. Thin film PV solar panels are made of 96-97% glass, 3-4% polymer, less than 1% semiconductor material, according to the International Renewable Energy Agency.
In 2010, the average solar panel used 13.3 kg of material per square meter, by 2020, this number had fallen to 6.2 kg per square meter, according to the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL).
This figure shows silicon-based solar panels’ components.

solar parts
What are Solar Panel Parts?
The following figure shows the main 9 parts of solar panels.

This following list explains the roles of the 9 solar panel’s components.
- Silicon Wafers. Silicon wafers are thin slices of crystalline silicon that form the basis of solar cells. Silicon is a semiconductor material. A semiconductor material is a material that has electrical conductivity between that of a conductor (such as metals) and an insulator (like rubber or glass)(Schroder, D. K. 2015). These wafer parts are usually quite pure, with impurities intentionally added to create a p-n junction, essential for converting sunlight into electricity.
- Metal Contacts. They are conductive metals (nickel, zinc, tin) that allow for the efficient collection and transmission of electricity generated by the solar panel’s photovoltaic (PV) cells. metal contacts are applied to the front and back of the silicon wafers. These contacts allow the flow of electrons when sunlight hits the solar cells.
- Encapsulation Materials.Solar panels are typically encapsulated in protective materials. Tempered glass encapsulates solar panels on the front side to protect the solar cells from weather and mechanical damage. A polymer-based back sheet encapsulates solar panels on the rear side to protect the cells from moisture and other environmental factors.
- EVA (Ethylene Vinyl Acetate). EVA is a copolymer made from two monomers. A layer of EVA film is put between the silicon wafers and the back sheet in solar panels. This film acts as an adhesive, bonding the components and protecting the solar cells.
- Frame. Solar panel frame material is the aluminium. Aluminium frames provide structural support and help protect the panel’s edges.
- Busbars and Ribbons. They are thin metal strips connect the individual solar cells in a panel, allowing the flow of electricity from one cell to another.
- Anti-reflective Coating. Solar panels have an anti-reflective coating applied to the glass surface. This coating part helps reduce the light reflected away, allowing more sunlight to reach the solar cells.
- Backing Sheet. The backing sheet is a part on the panel’s rear side offers additional protection and insulation for the solar cells.
- Bypass Diodes (for some panels). Bypass diodes are electronic components. Some solar panels have bypass diodes integrated into their design. These diodes help mitigate the impact of shading or partial cell failure on the overall performance of the panel.
When Were solar Panels Invented?
Solar panels were invented in 1881 by Charles Fritts the American inventor. Fritts’s panel was not very efficient and therefore not practical, where the efficiency was only about 1%.
To answer the question of who invented solar panels? In 1904, Reginald Fessenden, a Canadian inventor, invented a solar cell with an efficiency of about 10%. However, that cell was too expensive to be practical.
Then, the first truly efficient and practical silicon-based solar cell was developed by researchers Calvin Fuller, Gerald Pearson, and Daryl Chapin in 1954. This solar cell achieved a conversion efficiency of 6%, which was relatively high then.
What are the main types of solar panels?
The main 5 types of solar panels are in the following list.
- Bifacial Solar Panels
- Thin Film Solar Panels
- Monocrystalline Solar Panels
- Polycrystalline Solar Panels
- Passivated Emitter and Rear Cell (PERC)
The following figure shows the 5 main types of solar panel.

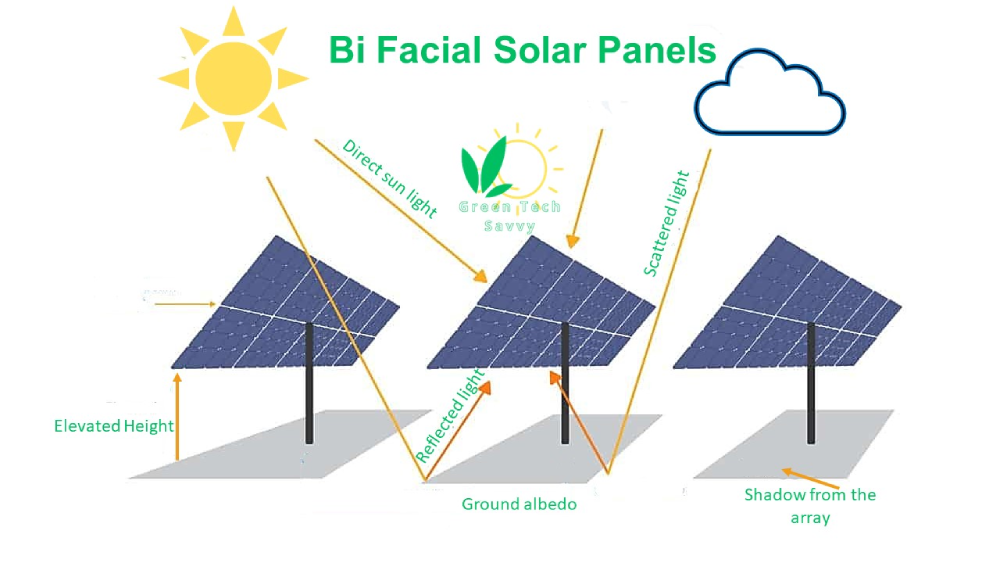
Bi Facial Solar Panels
Bifacial solar panels (double-sided solar panels) are a type of photovoltaic module that generate electricity from both sides of the panel (the front and rear surfaces). Bifacial solar panels are well-suited for environments with high Alberio, such as snowy areas or water bodies.
A bifacial panel can utilize the additional light reflected off surrounding surfaces, such as the ground, walls, or nearby structures.
To answer the question of “are bifacial solar panels worth it?” Bifacial panels are worth it only in places with additional light reflected off, snowy areas or near aquatic environments, where Bifacial panels increase energy generation, reduce Levelized Cost of Electricity (LCOE). LCOE is as a measure to evaluate the overall cost over the lifespan of generating electricity from solar energy.
Bifacial panels 3 disadvantages are in the next list.
- Complex to installation.
- Sensitive to shading.
- Limited rear-side absorption in areas with darker or shading.
A Bifacial solar module is shown in the following picture.
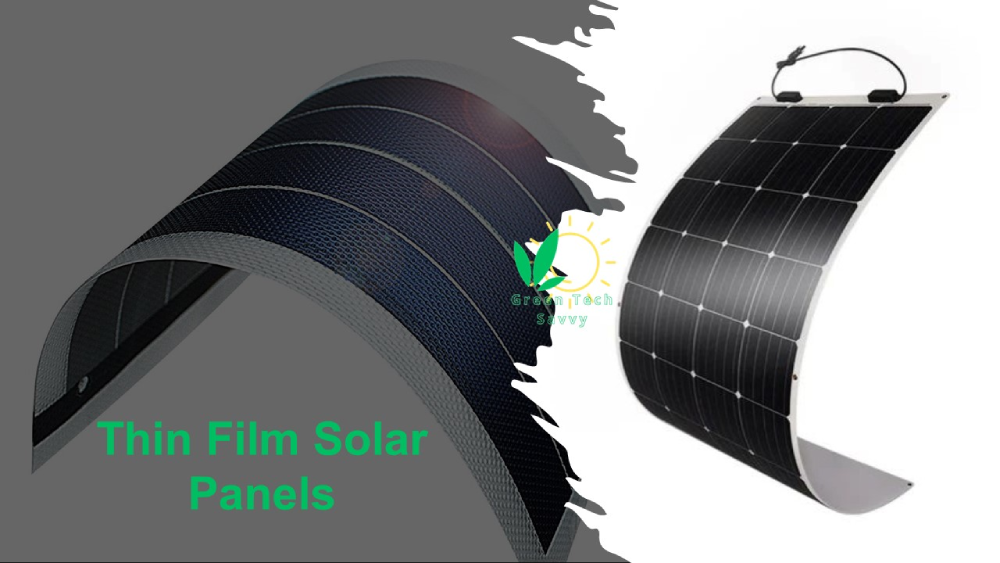
Thin Film Solar Panels
Thin film solar panels are a photovoltaic (PV) module that uses thin layers of semiconductor materials to convert sunlight into electricity.
Thin film solar cells are made by depositing extremely thin layers of semiconductor materials onto various substrates, while traditional crystalline silicon solar panels use thick layers of silicon wafers.
There are different types of thin film solar technology, each using a distinct semiconductor material. The most 3 common types of thin film solar technology are Amorphous Silicon (a-Si), Cadmium Telluride (CdTe), Copper Indium Gallium Selenide (CIGS).
The different types of thin film solar panels with different materials, have different characteristics (flexibility, lightweight, and efficiency). The most common types of thin-film solar panels include: Amorphous Silicon (a-Si), Cadmium Telluride (CdTe), Copper Indium Gallium Selenide (CIGS).
A thin film solar panel is shown in the following picture.
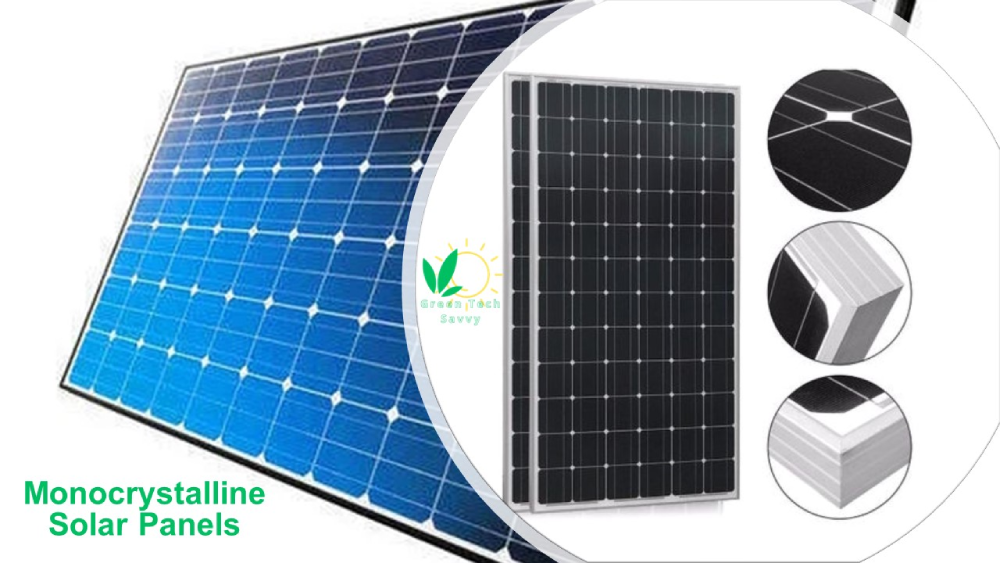
Monocrystalline Solar Panels
A monocrystalline solar panel is made up of solar cells that are created from a single, pure silicon crystal. This crystal is grown in a cylindrical shape and then sliced into thin wafers. The wafers are then cut into an octagonal shape to maximize their efficiency. The monocrystalline solar panel is characterized by the purity of the silicon crystals, and the black solar cells in them are nonadjacent. The actual efficiency of monocrystalline solar panels reach 22.8%, lasting for a minimum of 25 years. Also, monocrystalline panels require less space, and performance in low-light conditions.
Monocrystalline silicon pv panels are shown in the following picture.

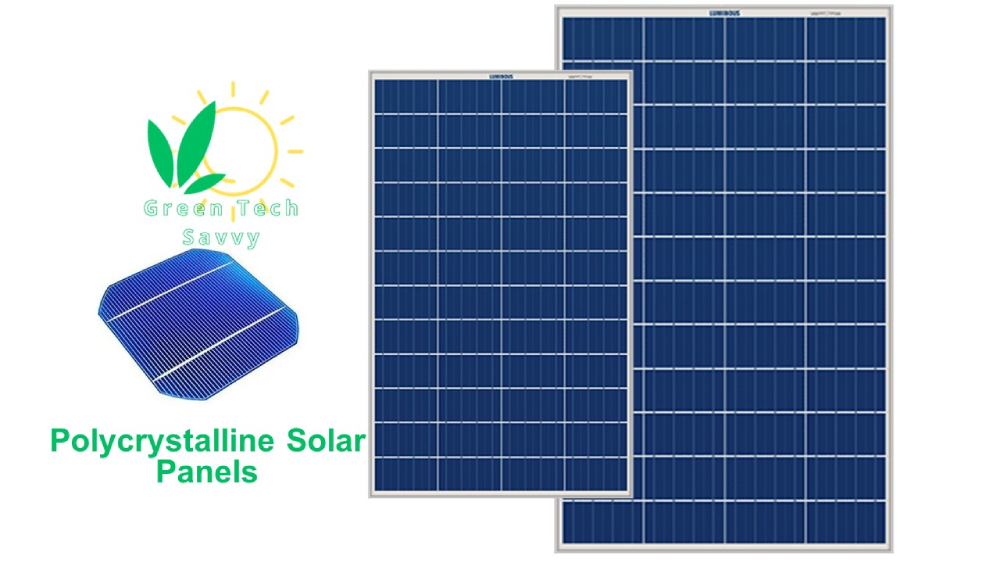
Polycrystalline Solar Panels
A Polycrystalline solar panel(Multi-crystalline solar panels) is a type of photovoltaic module made up of multiple silicon crystals that are melted together to form the wafers. These wafers are then cut into square shapes. The resulting panels have a mosaic-like appearance and a shining blue hue. Because there are multiple crystals in each cell, electrons have less space to move, resulting in slightly lower efficiency than monocrystalline panels. However, polycrystalline panels are less expensive to produce, making them a more affordable option. These panels are made from silicon. Polycrystalline solar panels efficiency reach 16.9%, its lifespan is 25 years at a minimum.
Polycrystalline photovoltaic panels are shown in the following picture.

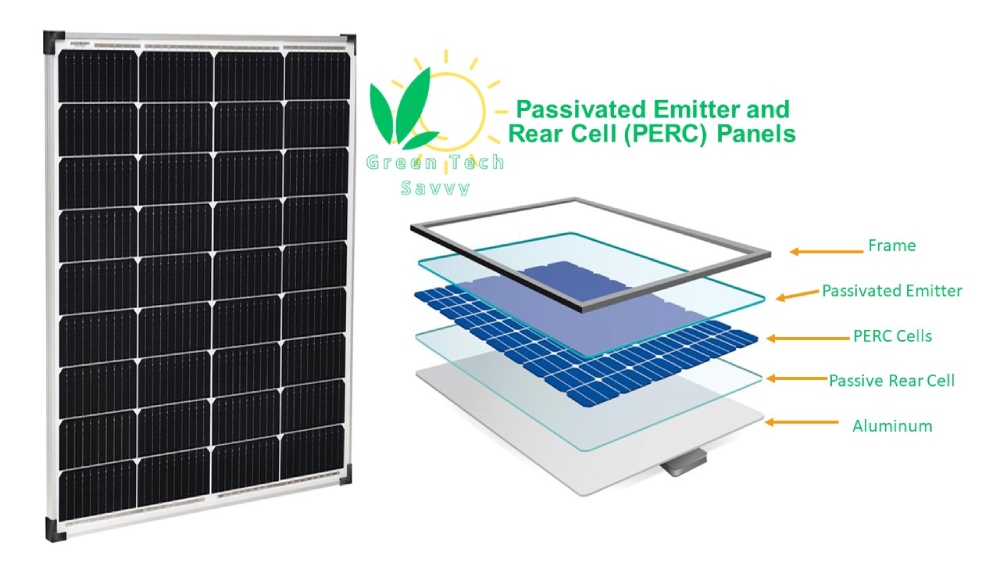
Passivated Emitter and Rear Cell (PERC) Panels
Passivated Emitter and Rear Cell (PERC) panels are an advanced type of solar panel technology that improves the efficiency of traditional photovoltaic cells. The PERC PV cell is improved traditional solar cell that have an extra layer on the backside. This extra layer, in perc solar cells, allows some of the sun’s rays that would normally be lost to bounce back into the solar cell, giving them another chance to be converted into electricity. As a result, PERC solar cells produce 6 to 12 percent more energy than conventional solar cells. PERC technology enhances the power output and performance of solar panels by modifying the cells’ structure, by using emitter layer, rear passivation layer, reflection and absorption.
A mono PERC solar panel refers to a monocrystalline solar panel that incorporates PERC (Passivated Emitter Rear Contact) technology. Mono PERC solar panels are designed to enhance the efficiency of energy conversion by incorporating a passivation layer on the rear side, minimizing electron recombination and improving the overall performance of the monocrystalline cell.
A PERC solar panel is shown in the following picture.

What are the Other Kinds of Solar Panels?
There are 5 different solar panels in the market. The following list explains the 5 different solar panels kinds in the market.
- Solar Panel Window Blinds (Transparent solar panels)
- Shingled solar panels
- Solar trees
- 3D Solar Panels
- Smart solar panels
the following figure shows the 5 main kinds of solar panel in the market.

Transparent Solar Panels (Solar Panel Windows)
Transparent solar panels (solar panel windows) (translucent solar panels) are an innovative type of solar technology that allows visible light to pass through while generating electricity from sunlight (clear panels). Transparent solar panels are integrated into windows, facades, and other transparent surfaces of buildings, vehicles, and various applications to harness solar energy without obstructing the view. Translucent solar panels are less efficient than traditional solar panels due to the need to maintain transparency.
The main feature of solar panels for windows (glass solar system) include:Transparent solar panels serve a dual purpose by acting as windows and electricity generators, enabling natural lighting and maintaining the view from the interior to the exterior while generating energy at same time.
The next picture shows a solar panel transparent and semi transparent solar panels.

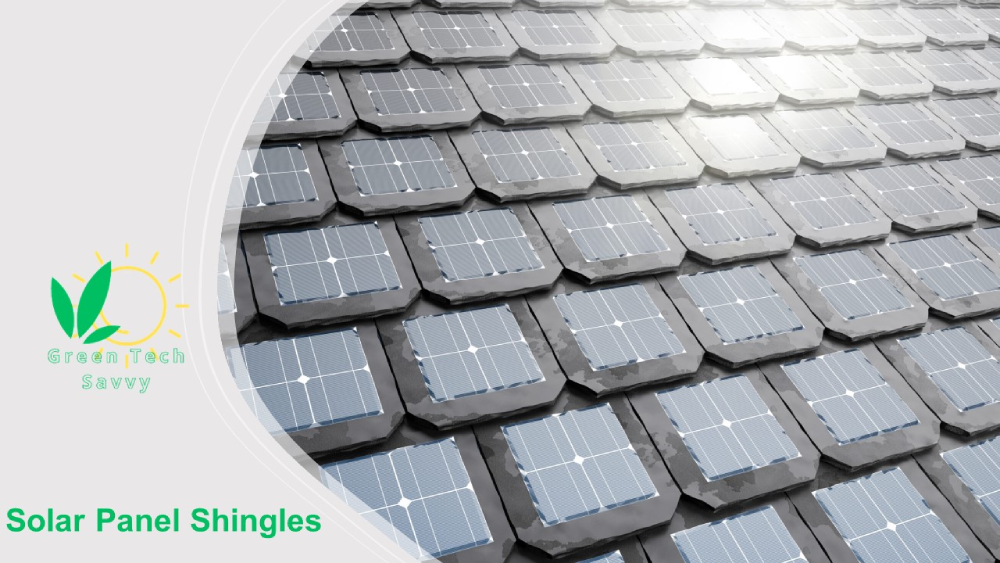
Solar Panel Shingles
Shingled solar panels (solar shingles) are solar panels have unique layout, where shingled solar panels are overlapped and interconnected, resembling the structure of roof shingles. Shingled solar panels design reduces energy loss, enhances overall panel efficiency, and offers other advantages compared to traditional solar panels.
5 main shingled solar panels benefits are in the next list.
- Save solar energy from loss. Solar roof shingles achieve efficiencies closer to the theoretical maximum, due to the overlapping of the solar cells.
- Work efficiently in high temperature. Solar shingles are affected less by increases in temperature.
- keep fixed production over the panel’s lifespan. That because a solar shingle exhibit lower degradation rates over time.
- Achieve higher power outputs within the same panel size. That because of the solar panel shingles’ enhanced efficiency.
- Perform better in partially shaded conditions. That due to how solar roofing shingles cells are interconnected.
The next picture shows solar panel roof shingles.

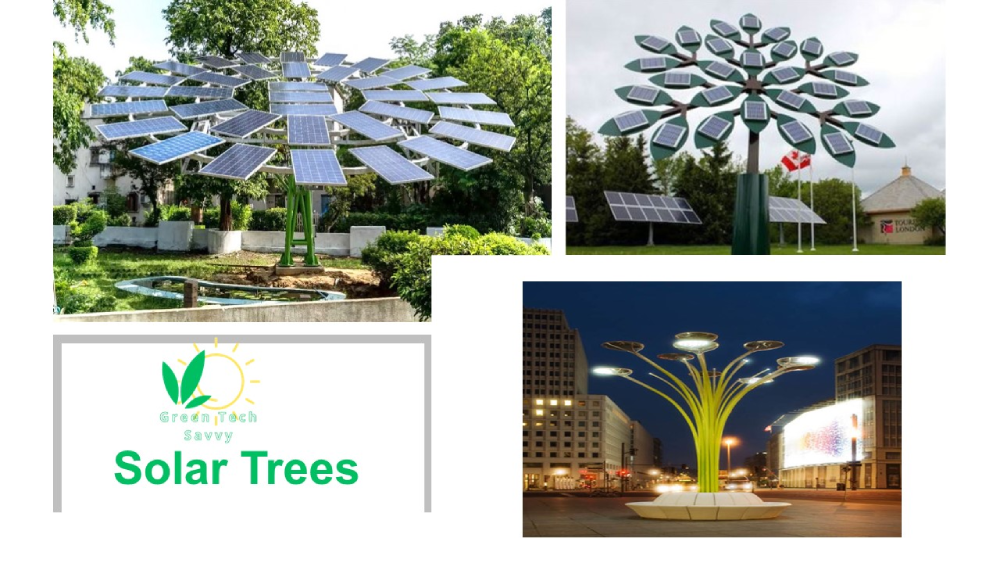
Solar Trees
A solar tree (solar power trees) is a structure designed to harness solar energy while providing shade and aesthetic appeal. Solar panel trees Use principles of biomimicry. Biomimicry in solar panels involves emulating principles observed in nature, such as the efficiency of photosynthesis, to improve the the performance and design of solar energy systems. Solar trees resemble trees in their design, with branches or panels extending outwards to capture sunlight. A power tree has advantages like (provide shade, able to be installed in various settings, and adaptability in size, configuration, and number of solar panels).
The next picture shows a power tree.

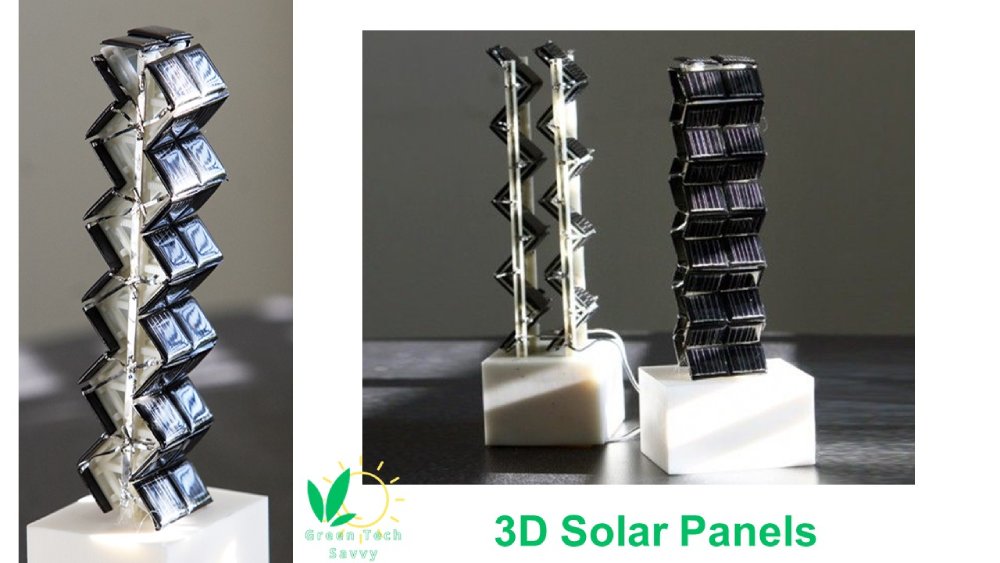
3D Solar Panels
3D solar panels are panels use additive manufacturing techniques, commonly known as 3D printing, to create solar energy harvesting devices.A 3d solar panel model uses a three-dimensional structure to boost photoelectric efficiency by increasing the amount of light absorbed by the light-absorbing material in the PV cell or panel. By using a3D solar panels design, the surface area available for light absorption is increased. Some designs also incorporate nanostructures such as wells, towers, or nanotubes, which are intended to trap photons, increasing the proportion that impart their energy to the PV cell.
The next picture shows 3D solar panels.
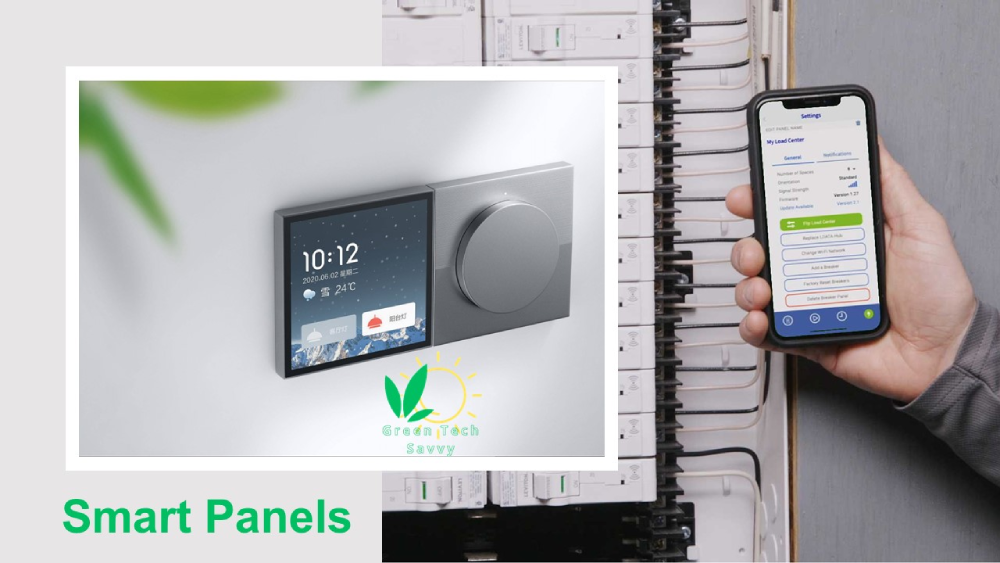
Smart Panels
A smart panel (intelligent solar panels) is a solar photovoltaic that incorporate advanced electronics, sensors, and communication capabilities to enhance their performance, monitoring, and integration with other systems. Solar edge panels go beyond the basic function of converting sunlight into electricity and offer additional features that optimize energy production, improve efficiency, and provide valuable data for analysis and control.
Smart solar panels provide 3 main benefits (collecting data, monitoring the system easily, and optimizing efficiency).
The next picture shows a smart panel.

What are Solar Arrays?
A solar array is a grouping or arrangement of multiple solar panels connected to generate electricity from sunlight. A solar panel array is a systematic layout of solar panels designed to maximize energy capture and efficiency as a part of solar panel systems.
A pv array is measured regarding its capacity to generate electricity, typically expressed in kilowatts (kW) or megawatts (MW). Solar panel arrays are used for various purposes, from powering individual homes to providing electricity for large-scale utility projects and commercial buildings.
Solar panel arrays vary from a few panels on residential rooftop systems to large installations covering acres of farm systems. Solar panel arrays are configured in various ways, depending on the available space, the desired energy output, and the installation’s specific requirements.
How to install a Solar Array?
Solar array installation is the process of mounting solar panels on a surface to generate electricity from sunlight. Solar arrays are configured in different methods. Solar arrays Installation is done on the roof of a building (Roof-mounted arrays). Or, solar arrays are installed on the ground, in an open area where they are angled optimally for maximum sunlight exposure (Ground-mounted arrays). Solar arraysare mounted on tracking systems that follow the sun’s movement throughout the day, ensuring that the panels face the sun directly (Tracking arrays).
What are Solar Panel Systems for Homes?
Home Solar panels systems (residential solar panels) are photovoltaic panels designed to capture sunlight and convert it into electricity for household use. Home solar panels systems have different capacities, and are grid connected or off grid.
A solar panels system for home includes Solar Panels, an inverter, batteries, and a tracking system. During their lifespan, home solar panel systems work, through the photovoltaic effect, to generate electricity that is used to power heating and cooling systems, lights, and more.
At the end of the lifespan of home solar panels systems, most of the materials used in solar panels are recyclable.
How do Solar Panels Work ?
Solar panels work when sunlight is made up of tiny particles called photons. When these photons hit a solar panel, they knock electrons free from atoms. The freed electrons then flow through the solar panel, creating an electric current. Solar panels work to capture this flow of electrons and turn it into usable electricity. Solar panels work through what is known as the photovoltaic effect.
What are Solar Panels Usages?
The primary purpose of solar panels is to generate electricity to power lights, cameras, appliances, electronics, heating and cooling systems, and other electrical devices commonly used in households.
One more usage of solar panels is to charge an electric vehicle (EV), such as electric cars and electric bikes.
Are Solar Panels Recyclable?
Yes, 90% of the materials in solar panels are recyclable, according to the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), and the National Renewable Energy Laboratory. Glass makes up about 75% of a solar panel’s weight, and glass recycling is already a common practice. Other easily recyclable materials include the aluminum frame, copper wire, and plastic junction box.
However, other materials in solar cells are more difficult to recycle (lead and cadmium). The polymer layers, that seal the solar panel from the weather, make recycling and disassembly difficult. This is because high temperatures are often needed to loosen the adhesive.